In Facilities Decommissioning operators technology plans are reporting adoption of Digital Technologies such as Predictive Decommissioning modelling, Scheduling & Optimisation. Access systems such as walk to work to allow decommissioning personnel to have accommodation on a vessel in the field reducing platform headcount, modular deck extensions to increase deckspace for well P&A and decommissioning.
Low cost external flotation systems to float off and tow jackets and topsides to shore for disposal. Diverless riser/pipeline separation by ROV tooling, adopting a factory approach to subsea Decom , use of low cost Anchor handling vessels for flowline and emerging now for structure recovery. novel technologies in waste management & Recycling – explosive collapse of structures to reduce height for improved access by remote machinery, marine ecology studies for subsea structures to better understand benefit or detriment to the marine environment of leave in place, conversion of recovered concrete mattresses into advanced paving systems for onshore re-use

Summary Findings – (Click on the Sub-Categories for detail)
- Survey & Planning –
Deployable technologies - Digital Technologies such as Predictive Decommissioning modelling, Scheduling & Optimisation, with Emerging Technologies looking into Marine Ecology and development of a Haptic Hand user interface to control large robotic systems in decommissioning - Late life Management & Equipment Readiness –
Operator focus is on Alternative power generation technologies and Peak load management to reduce emissions during late life and decommissioning phases, access systems such as walk to work to allow decommissioning personnel to have accommodation in the field without adding to platform headcount, modular deck extensions to increase deckspace for well P&A and decommissioning. - Topsides/Jackets Decommissioning
Topsides & Jacket Decommissioning is showing encouraging signs of novel cost saving methods from emerging technologies such as using external flotation systems to float off and tow jackets and topsides to shore for disposal, and Deployable Technologies such as re-usable modular grillages, modular access platforms and cutting technologies from well abandonment for topsides dismantling. - Subsea Equipment Decommissioning
Subsea Decommissioning – operators are adopting deployable technologies such as Crane deployed Utility ROV with specific decommissioning tooling skids, diverless riser/pipeline separation by ROV tooling, adopting a factory approach contracting strategy, and use of low cost Anchor handling vessels for flowline and emerging now for structure recovery - Site Inspection & Monitoring
Challenging the conventional thinking by looking at the impact on the environment of removal activities compared with benefits/Risks of “leave in place”. Energy efficient solutions to Guard installations without Guard Vessels, and low carbon solution with power generation, monitoring and comms. - Waste Management & Recycling
Operators are reporting some novel technologies in waste management & Recycling – deployable technology like explosive collapse of structures to reduce height for improved access by remote machinery, Emerging technologies include digital waste management and tracking, marine ecology studies for subsea structures to better understand benefit or detriment to the marine environment of leave in place, conversion of recovered concrete mattresses into advanced paving systems for onshore re-use
Facilities Decommissioning Technologies
- Over 50 technology plans submitted each year from 2018 to 2022
- Steady increase in number of individual technologies reported, however a reduction in the number of operators reporting interest in this area - Participation declining to Just 9 in 2022)
- A large number (45+) of respondents not yet considering this theme (based on submissions)
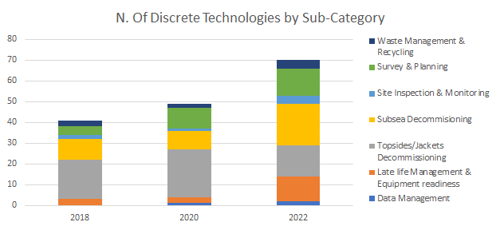
Facilities Decommissioning Technologies
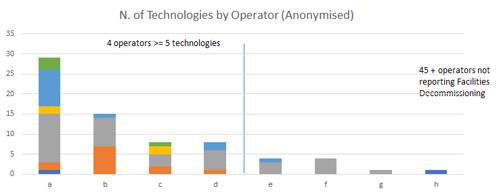
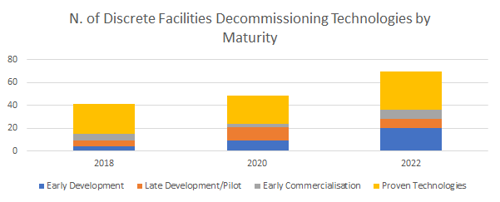
- Operators are focusing on a smaller number of technologies ready for deployment (Early Commercialisation TRL 8) and Existing or in widespread use (TRL 9)
- The pipeline of technologies under development (TRL 1-7) remains healthy
Evidence of maturity and deployments
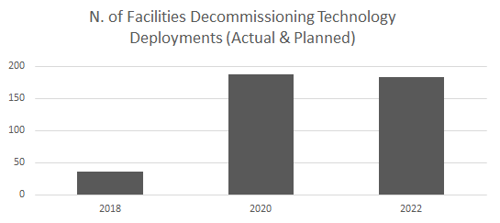
Once familiar with the technology the same operator deploys it at multiple assets (over 180 deployments reported/planned for 2021-23) Facilities Decommissioning remains a lagging technology category
1. Survey & Planning
In this sub-category operator focus is on Digital Technologies such as Predictive Decommissioning modelling, Scheduling & Optimisation, with Emerging Technologies looking into Marine Ecology and development of a Haptic Hand user interface to control large robotic systems in decommissioning
- Predictive Decommissioning Modelling -"Using Lone Star developed analytics tools”, it's possible to provide a 'living' mathematical model of complex organisations, providing decision makers with a near real-time 'what-if' scenario decision making capability
- CNR International (Ninian) ) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
Technology Example :
LoneStar Deepwater provides experienced project leads to manage or support every phase of the decommissioning and abandonment of existing offshore facilities.

- Virtual Emission Monitoring System (VEMS) - Decommissioning involves greater reliance on platform diesel generators, and vessel transportation. These two constitute over 90% of decommissioning related emissions, and therefore there is a need to better understand the true impact of them. VEMS will be an online emissions monitoring system for turbines, engines and marine vessels this AI-based tool utilizes operational parameters that are already collected by operators, and historical emissions measurements.
- CNR International (Ninian) ) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Software for Decom scheduling and optimisation - Software development to assess removal options, suitability of equipment and optimised plans.
- Harbour Energy (All Assets) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
- INSITE - Promote scientific research into marine ecology of structures to better understand their benefit or detriment to the marine environment (See further information in 6. Waste Management & Recycling)
- CNR International (Columba, B,D & E, Lyell, Thelma, Ninian & Strathspey) TRL 1-4 Early Development
- Haptic Hand - The proposed project aims to design and prototype a novel haptic hand as an effective and intuitive user interface to control a large robotic systems in decommissioning process."
- CNR International (Ninian) TRL 1-4 Early Development
2. Late Life Management & Equipment Readiness
Operator focus is on Alternative power generation technologies and Peak load management to reduce emissions during late life and decommissioning phases, access systems such as walk to work to allow decommissioning personnel to have accommodation in the field without adding to platform headcount, modular deck extensions to increase deckspace for well P&A and decommissioning.
- Walk to work - SMST modular gangway technology delivered ~ 90% uptime of fully connected gangway from CSV to platform when separating Ninian Northern topsides and jacket. Believed to be most Northerly application of walk to work.
- CNR International (Ninian) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Peak load management - Emissions Reduction - Utilising load bank and battery technology to manage peak load and reduce need for higher diesel generation requirements
- EnQuest (Broom) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Modular Deck Extensions - Expansion of Topside Deck Space to better perform Well P&A and Decom activities (avoid requirement for a TSV)
- TotalEnergies (Dunbar) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
Technology Example :
Modular Deck - Today’s highly competitive construction and maintenance programs demand bespoke methods of access that deliver the optimum levels of safety and efficiency. QuikDeck® can be built in the air, or on the ground and then hoisted into location. Using the equipment, workers feel safer which helps to improve productivity, but also heavy equipment can be moved around easily, even on wheels.
View Technology
- On/Offshore Collaboration Room - Facility to draw together on and offshore teams in a shared virtual working space
- EnQuest (Crathes) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Novel subsea tooling suite - Development of bespoke tooling suite through specialist contractor.
- Shell (Brent) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
- Alternative power generation - Specialised vendor to use alterative methods for power generation during and after platform habitation.
- EnQuest (Broom, Deveron, Heather) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
- Variable buoyancy system for subsea operations - Use of variable buoyancy system to deploy tooling at significant excursion from marine crane (alternative to air bags).
- Shell (Brent) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
3. Topsides & Jacket Decommissioning
Topsides & Jacket Decommissioning is showing encouraging signs of novel cost saving methods from emerging technologies such as using external flotation systems to float off and tow jackets and topsides to shore for disposal, and Deployable Technologies such as re-usable modular grillages, modular access platforms and cutting technologies from well abandonment for topsides dismantling.
- Topsides Single Lift - Review the use of the Pioneering Spirit for potential single lift opportunities.
- Apache (Beryl, Forties) CNR International (Banff, Ninian, Tiffany) Enquest (Broom, Heather, Thistle) Shell (Brent) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Reusable modular grillages - The re-usable modular grillage solution contributes to reducing greenhouse gases by being re-usable and scalable due to less steel required to be produced for bespoke systems as well as opening availability to more UK ports ? removing the logistic requirements to use ports overseas.
- Harbour Energy (All Assets) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- QuikDeck Access - AquaTerra - Modular Alternative access systems, gives increased deck space for Decommissioning and well P&A activities (See 2. late life Management & Equipment Readiness)
- Fairfield (Dunlin) TRL 8 Early commercialisation
- Control Cutter for Conductor recovery - Decom tool to shear multiple string casings at surface ,rather than traditional methods
- EnQuest (Heather, Thistle) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
- Keops-Platform Lifting and Transportation System - Phase 1- (NZTC) - Alternative method of fixed platform removals (jacket+topsides), without using a HLV , using an external flotation system to float-off and tow the full platform, to a nominated reception facility, for disposal.
- Repsol Sinopec Resources (Beatrice) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
Technology Example :
transport to shore capability Allseas Pioneering Spirit – Single lift vessel with unique Topsides and Jacket removal systems, combined with Simultaneous Topsides and Jacket
View Technology
- Crane-free decommissioning - Generally the structures are not precious following decom, and yet there is high risk to essentially just reverse install structures. This proposes an anchor handler for recovering small structures (up to circa 200-300Te) using the anchor handling winch as an alternative lifting device and then transporting them to shore by towing. Operator intends to examine these aspects and develop a preferred solution to these challenges.
- CNR International (Ninian) TRL 1-4 Early Development
4. Subsea Decommissioning
Subsea Decommissioning – operators are adopting deployable technologies such as Crane deployed Utility ROV with specific decommissioning tooling skids, diverless riser/pipeline separation by ROV tooling, adopting a factry approach contracting strategy, and use of low cost Anchor handling vessels for flowline and emerging now for structure recovery
- Utility ROV - During decommissioning all traces of oil and gas material needs to be removed from the seabed in the 500m zones around the platform locations. Traditionally, would have been carried out utilising various techniques by Work Class ROV and Divers. Novel Crane deployed ROV with a "swiss army knife" skid which can be adapted for all sorts of subsea decommissioning. Utilised primarily for mattress and export line and debris recovery. (UTROV)
- Harbour Energy (All Assets) Neptune Energy (Juliet & Minke) Repsol Sinopec Resources (Buchan) TRL9 Proven Technologies
Technology Example :
Utility ROV Services were contracted by Boskalis Subsea to aid with decommissioning works on Neptune Energy E&P UK’s Juliet and Minke fields. The work scope consisted of the following; de-burial of assets, recovery of concrete mattresses, cutting and recovery of pipeline, spools & flexibles, clearance of debris and burial of exposed pipeline ends – all in 40-60 metres of water.
View Technology
- Subsea diverless flexible riser / pipeline separation - Subsea ROV deployed tool cut through flange bolts enabling pipeline / riser to be separated and pipeline then capped for future use with ROV deployed expanding plug
- CNR International (Banff, Kyle Ninian, Thelma, Tiffany, Toni) TRL9 Proven Technologies
- Anchor handling vessel used for Flowline recovery - Bundle cutting and towhead recovery, Flowline Recovery
- TotalEnergies (Ballindalloch, James) TRL 9 – Proven Technologies
- Adopting a factory approach - New/alternative contracting strategies to carry out removal of subsea infrastructure in a factory approach rather than piecemeal
- TotalEnergies (Tullich) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Crane-free decommissioning - Generally the structures are not precious following decom, and yet there is high risk to essentially just reverse install structures. This proposes an anchor handler for recovering small structures (up to circa 200-300Te) using the anchor handling winch as an alternative lifting device and then transporting them to shore by towing. Operator intends to examine these aspects and develop a preferred solution to these challenges.
- CNR International (Ninian) TRL 1-4 Early Development
- Accelerated Corrosion (NZTC) - Aim of this technique is to avoid subsea infrastructure removal and onshore disposal, but leaving a clear seabed of subsea infrastructure by dissolving steel based structures accelerating the speed of seawater corrosion
- Repsol Sinopec (Beatrice) TRL5-7 Late Development/Pilot
5. Site Inspection & Monitoring
Challenging the conventional thinking by looking at the impact on the environment of removal activities compared with benefits/Risks of “leave in place”. Energy efficient solutions to Guard installations without Guard Vessels, and low carbon solution with power generation, monitoring and comms.
- Integrated Engineered Reefs - The idea is to change the conversation from Sea dumping to Habitat building by putting more structure in. Australia are re-engineering retired assets and integrating them into purpose built reefs. Instead of removing these valuable habitats, enabling operators to super charge them by putting more in
- CNR International (Ninian) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Cardinal buoys in lieu of guard vessels - Offshore deployment of cardinal buoys to mark partially decommissioning structures as safe cost efficient solution; already deployed at NNP and Banff & Kyle
- CNR International (Banff, Kyle, Ninian) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Permanent Artificial Reefs for Pipeline Protection - More environmentally robust pipeline/cable protection is required for future Oil & Gas subsea developments or decommissioned infrastructure protection that does not add to the ocean’s micro-plastic inventory. This project will evaluate the benefits of creating Artificial Reefs using the patented “Reef-Cube” design and fully develop the “Reef-Bag”, “Reef Matt” & “Grout-EcoBag” products as pipeline/cable protection and prove the potential to use recycled decommissioned concrete mattresses and rock bags in their manufacture.
- CNR International (Ninian) TRL 9 Proven Technology
Technology Example :
Arc Marine reef cubes® are designed to support and protect life on our seafloor and coastlines and can be utilised across various industries, including aquaculture, coastal defence, reef conservation, eco-engineering and subsea protection.
View Technology
- Topsides Cell Access - Bespoke ROV tooling to intervene on previously inaccessible pipework inside base of concrete leg to recover potential trapped hydrocarbons.
- Shell (Brent) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
- Power Buoy - Buoy which generates autonomous, renewable energy from wave motion and enables communication, data transfer and remote operation via VSAT. Could be used to power subsea field equipment and monitor exclusion zones
- Harbour Energy (Huntington) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
- Navaid - Brent Charlie leg height after topsides lift will be circa +8m, which is too low for a conventional GBS navaid. Base case option is to install an additional concrete tower but marine buoys will be investigated as an alternative.
- Shell (Brent) TRL 1-4 Early Development
6. Waste Management & Recycling
Operators are reporting some novel technologies in waste management & Recycling – deployable technology like explosive collapse of structures to reduce height for improved access by remote machinery, Emerging technologies include digital waste management and tracking, marine ecology studies for subsea structures to better understand benefit or detriment to the marine environment of leave in place, conversion of recovered concrete mattresses into advanced paving systems for onshore re-use
- Explosive collapse of structures - Using explosive technology to reduce the height of structures delivered onshore from dismantling. The technology can reduce working at height risk and facilitate access by remote machinery to safely progress dismantling work.
- CNR International (Ninian, Tiffany) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Radtrac - Radtrac by WasteVu. Digitalising the waste tracking & management process. Improve tracking & reduce incidents. Improved transparency & visibility & improved data quality & reporting
- Shell (Curlew B+D, and C) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
- INSITE - Promote scientific research into marine ecology of structures to better understand their benefit or detriment to the marine environment
- CNR International (Banff, Kyle) TRL 1-4 Early Development
Technology Example :
INSITE Scientific Research The North Sea is one of the busiest stretches of water in the world and the extent of human activities both above and below the surface has been well documented. The many nations that border the North Sea have established a track record of studying its waters. The many structures that occupy the predominantly sandy seabed of the North Sea have been of interest to institutions across Northern Europe specialising in marine science.
View Technology
- Conversion of concrete mattresses into advanced permeable paving systems for storm-water management - This proposal seeks to revolutionise the disposal of concrete mattresses by taking a circular economy approach - developing them into advanced permeable paving systems which can play a key role in alleviating flooding across the UK.
- CNR International (Ninian) TRL 1-4 Early development



