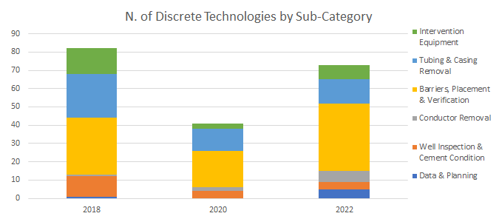
Following a significant fall off in 2020, Well P&A is showing an increase in reported number of technologies in 2022 data. Collaboration for Well P&A campaigns. Thru tubing logging, down hole wireless sensing.
Hydraulic severance equipment to adopt a factory approach to conductor and casing string removal. Increase in novel Alternative Barrier techniques Reducing costs by Light Well Intervention Vessel Techniques (LWIV) for subsea open-water abandonments. High quality solutions for improving well access for interventions - low cost platform workover rigs/modular drilling rig systems

Summary findings (CTRL + Click on Sub-Category for detail)
- Data & Planning
Operator focus is on low cost intervention, efficient well P&A operations, collaboration for Well P&A campaigns, data logging for well planning. - Well Inspection & Cement Condition
Operator focus is on thru tubing logging, down hole wireless sensing, FLI inspection techniques and novel well head sealing techniques. - Conductor Removal
Hydraulic severance equipment to adopt a factory approach to conductor and casing string removal, and emerging technologies for novel cutting techniques – subsea laser cutting and novel application of diamond wire cutting in a dedicated Well Head cutting Tool. - Barriers, Placement & Verification
Operator’s are using deployable technologies such as Thru Tubing Abandonment, PWC (Perf Wash & Cement), Shale barriers and Fusion Based Alloy, and in emerging technologies Piloting large scale trials of novel abandonment techniques - Tubing & Casing Removal
Operator’s increasingly looking at reducing costs by Light Well Intervention Vessel Techniques (LWIV) for subsea open-water abandonments, 2 emerging technologies for breaking the cement bond on casing string, and novel cutting using explosive and propellant fuelled technologies - Intervention Equipment
sub-category continues to show high quality solutions for improving well access for interventions - low cost platform workover rigs/modular drilling rig systems
Well Plugging & Abandonment technologies
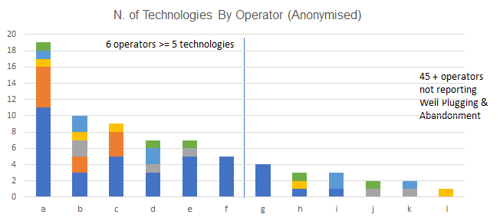
- Over 50 technology plans submitted each year from 2018 to 2022
- Steady Decline in number of individual technologies reported, together with the number of operators reporting interest in this area (Participation declining from 24 operators in 2018 to 14 in 2022)
- A large number (45 +) of respondents not considering this theme (based on submissions)
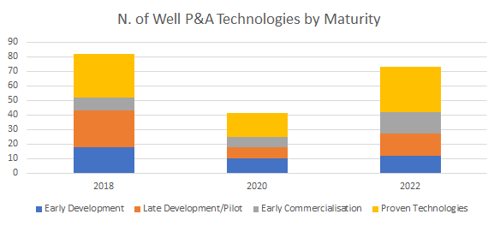
- Operators are focusing on a smaller number of technologies ready for deployment (Early Commercialisation (TRL 8) and Existing or in widespread use Technologies (TRL 9)
- Growing pipeline of solutions remains healthy (TRL 1-7)
Maturity and deployments
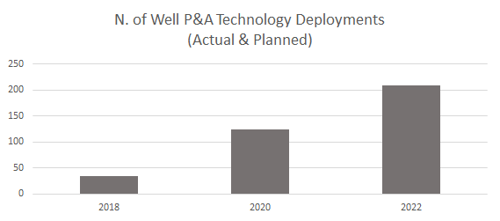
Once familiar with the technology the same operator deploys it at multiple assets (over 300 deployments reported/planned for 2021-23)
1. Data & Planning
In this sub-category operator focus is on low cost intervention, efficient well P&A operations, collaboration for Well P&A campaigns, data logging for well planning.
-
- Application of Tie line - Use of a survey tie line in order to remove the requirement for a separate borehole to be drilled at the well locations. Includes debris clearance and shallow gas surveys.
- Neptune (Minke, Orca)
- WellSense - "Rigless leak investigation through noise logging“ DAS – Distributed Accoustic Survey
- Shell (Brent)
Technology Example :
Well Sense DAS survey - rigless leak investigation through noise logging, typical acoustic signature of a leak in the wellbore.
View Technology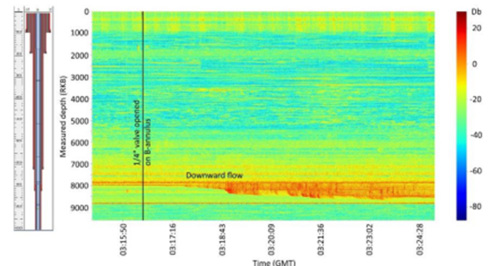
- Space Tool - Ultrasonic Logging Tool: Logging tool which looks ahead of travel
- TotalEnergies (Janice)
- Wellsafe Guardian Rig for P&A - Potential identification of the WSG rig to complete well decommissioning. The rig is specifically designed for decommissioning in the UK, including: Dedicated P&A vessel and crew, On-board 12 person saturation diving system with ROV
- Apache (Beryl, Forties) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
- Application of Tie line - Use of a survey tie line in order to remove the requirement for a separate borehole to be drilled at the well locations. Includes debris clearance and shallow gas surveys.
- E&A well abandonment collaboration - Collaborative project to stimulate supply chain to develop cost efficient P&A of E&A wells
- Ithaca (Captain) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
2. Well Inspection & Cement Condition
Well Inspection and Cement Condition – Operator focus is on thru tubing logging, down hole wireless sensing, FLI inspection techniques and novel well head sealing techniques.
- Expro CATS Pressure Gauge - Pressure monitoring of abandoned wells. Planned to be used on a tertiary exploration well in 2020 to assess depletion of the reservoir sands during an extended production test on an adjacent well.
- Apache (Beryl) (TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Wellhead Integrity management - Novel wellhead sealing for production wells due to integrity issues
- EnQuest (Magnus) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Probe - Assess cement through multiple strings by Thru-Tubing Logging
- Total Energies (Culzean, Alwyn North) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
- Well Sense Tool - Tool to review condition of the well bore. FLI Tool deployed on Fibreline to review well bore.
- DNO (Ketch) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- DNO (Ketch) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
Technology Example :
Well Sense FLI tools - length of fibre that can be unspooled from a FLI probe to 7,715m, We can supply Active-FLI probes, fitted with electronic sensors and optical telemetry. FLI is primarily designed to be a distributed sensing system, observing the wellbore simultaneously along the entire length of the unspooled fibre.
View Technology
- Schlumberger - CETT logging tool - Schlumberger - CETT logging tool for through tubing logging to assess cement quality behind the production casing.
- Harbour Energy (Bell) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
3. Conductor Removal
Conductor Removal Technologies : one deployable technology - hydraulic severance equipment to adopt a factory approach to conductor and casing string removal, and emerging technologies for novel cutting techniques – subsea laser cutting and novel application of diamond wire cutting in a dedicated Well Head cutting Tool.
- Hydraulic severance of conductor and casing strings - Successfully completed by other operators using Control Cutter. Consider this technology for when CNR's other fixed installations approach their CoP, also used by other operators listed below.
- CNR International (Banff), DNO (Ketch), Harbour Energy (Bell), Perenco (Amethyst) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Subsea Laser Cutting - Less mechanical parts required as part of laser system and as such less project risk
- EnQuest (Crathes) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
Technology Example :
Control Cutter - Our Conductor Decom Package includes all equipment and calculations required to recover the wellhead and conductors. We section the multistring casing into the required lengths then lift, handle and prepare the sections for backloading. Our cutting and pinning tooling is incorporated into a single interface frame/table.
View Technology
- Wellhead Cutting Tool – DeepOcean is currently designing and developing an innovative Wellhead Cutting Tool (WHCT), DeepOcean proposes a WHCT with control of all cutting parameters, including verification of a completed cut. The system is based on a diamond wire technique removing the need for compressed air. and combined with a smaller spread with less personnel on board, reduces decommissioning costs for operators.
- CNR International (Banff) TRL 1-4 Early development
4. Barrier Placement & Verification
Barrier Placement & Verification – operators are using deployable technologies such as Thru Tubing Abandonment, PWC (Perf Wash & Cement), Shale barriers and Fusion Based Alloy, and in emerging technologies Piloting large scale trials of novel abandonment techniques
- Hydrawell PWC - Utilise PWC - Jetting Nozzle Type as a viable abandonment technique, taking advantage of in-house CFD analysis to remove the requirement for drill-out verification
- Harbour Energy (Bell) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
Technology Example :
Spirit Energy are the lead sponsor of a TLB Industry sponsored programme to deliver bulk field trials of alternative barrier P&A solutions. To accelerate adoption of alternatives to traditional cement based approaches and promoting the use of rig less well abandonment techniques with potential for considerable cost savings
View Technology
- Through tubing abandonment (TTA) utilising tubing rotation -Significantly reduce cost of P&A and Rig days requirement via implementation of the TT enablers
- Shell (Brent) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Shell (Brent) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Shale Barriers Collapsing shales in Balder/Hordaland Formation on MacCulloch - transferrable to other CNS wells. Avoid the need to perform remedial work on wells where production casing straddles collapsible formations (shales/salts)
- Harbour Energy (All Assets) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- LWIV subsea well P&A - barriers - Viscous gel plug as base for setting tubing and annular cement barrier in subsea well allowing LWIV only abandonment
- CNR International (All Assets) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Fusion Based Alloy Thru Tubing Abandonment “ Low cost field trials” - New model for low cost field trials to be developed by collaborating with other operators.
- Spirit Energy (All Assets), TotalEnergies (All Assets), Harbour Energies (All Assets) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
- Shale Barrier Predictions - Create pseudo DCM analysis to predict abandonment barriers from conventional log data
- Shell (All Assets) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
- Plastic deformation of casings to create an environmental well barrier - Potentially more efficient than conventional use of cement for non-pressure retaining environmental well barrier
- CNR (All Assets) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
5. Tubing & Casing Removal
A range of deployable technologies for Tubing & Casing Removal – operators increasingly looking at reducing costs by Light Well Intervention Vessel Techniques (LWIV) for subsea open-water abandonments, 2 emerging technologies for breaking the cement bond on casing string, and novel cutting using explosive and propellant fuelled technologies
- LWIV subsea well abandonment - Open hole 300' tubing cut, recovery and layout on seabed for subsequent uplift by CSV allows LWIV only subsea well abandonment
- CNR International (Banff) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Subsea Open Water P&A - Through-Tubing P&A with an LWIV. Including recovery of tubing hanger and surface tubing to allow setting of environmental plug.
- Shell (Pierce) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Control Cutter – Also applicable o this sub-category - Bespoke shearing device for surface multi string cutting during phase 3 abandonment operations (see 3. Conductor removal for more details)
- Shell (Brent) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Rotojar (Re-branded HydroVolve Hammer) - Improve jarring operations by combining high overpull forces with high frequency vibration to improve stuck-object extraction force regime available to the stuck casing on HWU
- Shell (Brent) TRL 8 Early commercialisation
Technology Example :
HydroVolve Hammer – combined pulling and impact forces to break settled solids and shear cement bonds. The ability to induce resonance to the casing to significantly increase the dynamic action on stuck structure. Combining high overpull forces with high frequency vibration to deliver the an effective stuck-object extraction force to remove stuck casing.
View Technology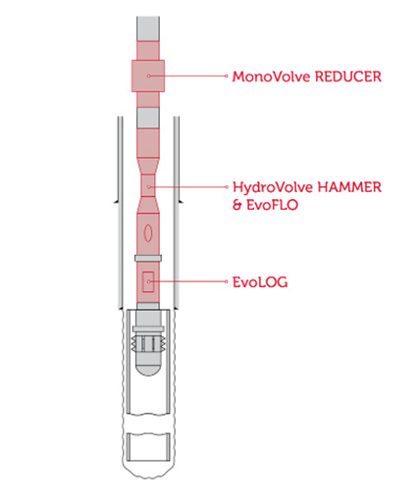
- Deep casing Tools "Casing Cement Breaker" - Mechanical device to manipulate a casing string in order to break the cement bond between casing and cement or barite and facilitate deep casing recovery.
- TotalEnergies (Ballindalloch) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
- SPEX Lattice Cutter - An explosive charge which is used as an alternative to milling
- TotalEnergies (Alwyn North, Ballindalloch) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
- Prometheus - Similar to a Lattice Cutter, propellent fueled tool intended for through tubing metal removal for Thermal Casing removal
- TotalEnergies (Alwyn North, Ballindalloch) TRL 5-7 Late Development/Pilot
6. Intervention Equipment
Intervention Equipment sub-category continues to show high quality solutions for improving well access for interventions - low cost platform workover rigs/modular drilling rig systems.
- Rig configured specifically for well P&A – using WSS to deliver transformational subsea well P&A with their rig designed for that purpose
- CNR International (Banff) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- MARS System – - OneSubsea MARS* multiple application reinjection system serves as a universal interface for trees (topside and subsea), enabling fluid communication between the existing isolation barriers.
- (Dana/KNOC - Bittern) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
Technology Example :
OneSubsea MARS - providing low-cost, low-risk intervention - cost-effective wellhead processing. MARS system technology can be used for both vertical and horizontal production trees in surface and subsea applications.
View Technology
- Bore Selector - Selector for triple bore well operations. Enovate.
- TAQA (South Cormorant) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- TAQA (South Cormorant) TRL 9 Proven Technologies
- Striecher Modular Drilling Systems – Offshore Models - Streicher modular system - Fully Automated Offshore Drilling Rig
- Harbour Energy (all assets) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
Technology Example :
Striecher Modular Drilling Systems – Offshore Models - Streicher modular system - Fully Automated Offshore Drilling Rig, two sizes to suit application VDD400 offshore and VDD 200 offshore , Modular Construction, Simple Rig Assembly and Disassembly under Offshore Conditions, Two Direction Skidding.
View Technology
- Micro Coil - Potential to deploy plug in short string tail pipe without a full wireline PCE rig up
- TAQA (Tern) TRL 8 Early Commercialisation
- Rigless P&A - To avoid lifting hundreds of ft of tubing to surface, the technology comprises a hydraulically driven slips and cutting module located on the seabed. The cutting tool would connect to a pressure control equipment via an H4 connector or similar. The cutting tool/slips would be located above the pressure control equipment. Handling would involve a crane and ROV. The ROV would fly over hot stab to control cut and slips etc. Cut tubing joints would be laid out into subsea baskets.
- CNR (Ninian) TRL 1-4 Early Development



